FastAPI - 05 (쿼리 매개변수와 문자열 유효성 검사)
출처: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/query-params-str-validations/
아래의 내용은 공식 사이트의 내용을 제 경험과 생각을 추가하여 다시 정리한 것 입니다.
선택적 쿼리 매개변수
쿼리 매개변수 q를 필수가 아닌 선택적으로 만들기
from typing import Union # 여러 타입 중 하나를 지정하기 위해 Union 사용
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# q의 타입을 Union[str, None]으로 지정
# q의 기본값을 None으로 지정
# q는 선택적으로 만들어짐
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
FastAPI - 03 (쿼리(Query) 매개변수) 참조
Query, Annotated 사용
Annotated를 사용하여 쿼리 매개변수의 유효성 검사를 할 수 있습니다.
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query # Query import
from typing_extensions import Annotated # Annotated import
# python 3.10
# from typing import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# Query(max_length=50) - 쿼리 매개변수의 최대 길이를 50으로 지정
# Union[str, None]와 Query(max_length=50)을 Annotated로 묶음
# 기본값을 None으로 지정
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
쿼리 매개변수 q의 최대 길이를 50으로 지정하고, 기본값을 None으로 지정합니다. q의 길이가 50을 초과하면 422 Unprocessable Entity 오류가 발생합니다.
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901
{
"detail": [
{
"loc": [
"query",
"q"
],
"msg": "ensure this value has at most 50 characters",
"type": "value_error.any_str.max_length",
"ctx": {
"limit_value": 50
},
"url": "https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.4/v/string_too_long"
}
]
}
FastAPI version 0.95.0 이상에서는 Annotated를 사용할 수 있습니다.
q: Union[str, None] = None
# Union[str, None]을 Annotated로 묶음
q: Annotated[Union[str, None]] = None
위의 두 코드는 같은 의미입니다.
Query로 default 값 지정
Query를 사용하여 쿼리 매개변수의 기본값을 지정할 수 있습니다.
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# q의 default 값을 "default query"로 None을 지정
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
q: Union[str, None] = None
# python 3.10
# q: str | None = None
q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None)
위의 두 코드는 같은 의미입니다.
q: Annotated[str, Query(default="rick")] = "morty"
위와 같이 방법은 기본값이 “rick”인지 “morty”인지 명확하지 않기 때문에 허용되지 않습니다.
Union[str, None] 부분을 사용하면 편집기에서 더 나은 지원을 제공합니다.
Annotated 사용 권장
- 일관성과 직관성
Annotated는 Python 함수의 기본값(default value)을 그대로 사용합니다. 이는 Python에서 일반적으로 사용되는 방식에 더 부합하며, 코드를 이해하고 작성하는 데 더 직관적입니다. - 다양한 환경에서의 호환성
Annotated를 사용하면 FastAPI 외의 다른 환경에서도 같은 함수를 호출할 수 있으며, 예상대로 작동합니다. 필수 매개변수(기본값 없음)가 있다면, 편집기나 Python 실행 시에 필요한 매개변수가 누락되었을 때 오류를 통해 알려줍니다. - 오류 방지
기존의 기본값 스타일을 사용하지 않고 Annotated를 사용하면, FastAPI 외부에서 해당 함수를 호출할 때도 올바른 인자를 전달해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 기대와 다른 값(e.g. QueryInfo 대신 str)이 전달될 수 있으며, 이는 함수 내부의 연산에서 오류가 발생할 때까지 파이썬이나 편집기에서 경고를 주지 않습니다.
다양한 유효성 검사
min_length
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
# min_length: q의 최소 길이를 3으로 지정
q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3, max_length=50)] = None
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
정규 표현식(regex)
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
# pattern: q의 패턴(정규식)을 지정
Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$")
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
^: 다음 문자로 시작하며 앞에 문자가 없습니다.
fixedquery: 정확한 값이 있습니다 fixedquery.
$: 여기서 끝나고 fixedquery. 뒤에는 더 이상 문자가 없습니다.
정규 표현식은 많은 사람들이 어려워합니다. 그리고 정규 표현식이 없어도 많은 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
기본값
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# q의 기본값을 "default query"로 지정
# None을 포함 해서 기본값이 지정 되면 매개 변수는 선택사항이 됩니다.
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str, Query(min_length=3)] = "fixedquery"):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
필수로 지정
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# q의 기본값을 선언하지 않으면 필수로 지정됩니다.
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str, Query(min_length=3)]):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
줄임표(Ellipsis)(…)로 필수 선언
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# ...을 사용하여 필수로 지정
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str, Query(min_length=3)] = ...):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
...(Ellipsis)는 실제로 특별한 목적을 가진 내장 상수입니다.- 필수 매개변수 표시: q가 필수 매개변수임을 나타냅니다. q 매개변수에 대한 인자를 제공하지 않으면 Python은 오류를 발생시킵니다.
- 기본값의 부재: 일반적으로 함수 매개변수에 기본값을 제공하지 않으면, 그 매개변수는 필수적으로 값을 제공해야 합니다.
- 문서화 및 가독성 증진: 코드의 가독성을 높이고, 개발자에게 특정 매개변수가 의도적으로 값을 생략했음을 알리는 데 사용됩니다.
None을 허용하지만 필수로 지정
None을 허용하지만 기본값을 (…)로 지정하여 필수로 지정할 수 있습니다. None을 보내서라도 쿼리 매개변수를 보내야 합니다. 값을 보내지 않으면 오류가 발생합니다.
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# Union[str, None]로 None을 허용
# 기본값을 ...로 지정하여 필수로 지정
# None을 보내서라도 쿼리 매개변수를 보내야 함
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3)] = ...):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
List형의 쿼리 매개변수
from typing import List, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
# List[str]로 q를 List형으로 지정
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[List[str], None], Query()] = None):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?q=foo&q=bar
위와 같이 호출하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나옵니다.
{
"q": [
"foo",
"bar"
]
}
아래는 API 문서의 예시 입니다.
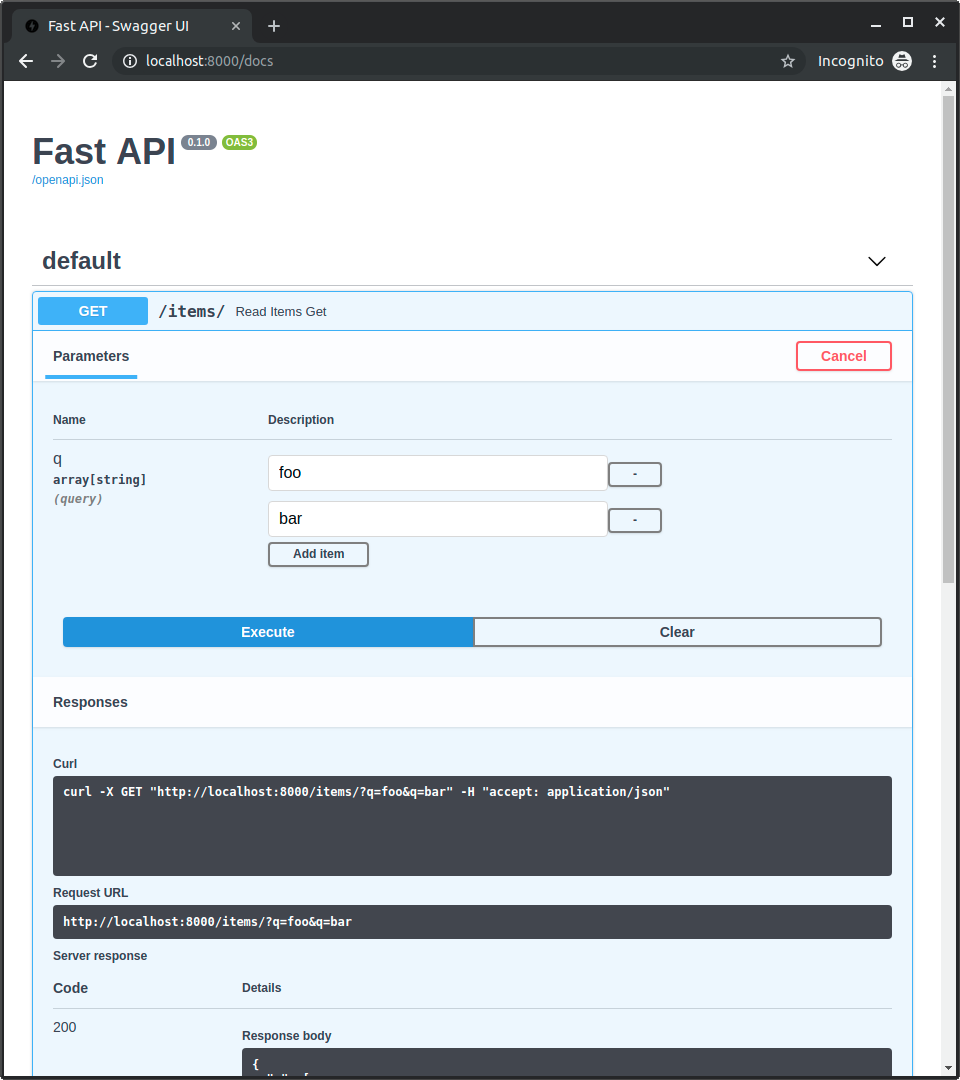
List의 기본값
from typing import List
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[List[str], Query()] = ["foo", "bar"]):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/
위와 같이 호출하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나옵니다.
{
"items": [
{
"item_id": "Foo"
},
{
"item_id": "Bar"
}
]
}
그 외의 메타데이터
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
from typing_extensions import Annotated
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
Union[str, None],
# title: q의 제목을 지정
# description: q의 설명을 지정
# min_length: q의 최소 길이를 3으로 지정
Query(
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
),
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
위 코드에서 read_items 함수에는 q라는 쿼리 매개변수가 있으며, 이 매개변수에 대한 title은 “Query string”이고, description은 “Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match”입니다. 이 정보는 FastAPI에 의해 생성되는 API 문서(http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs)에 표시되어 사용자가 이 쿼리 매개변수의 목적을 이해하는 데 도움을 줍니다.
해시태그: #fastapi #uvicorn #fastapi Query #fastapi Annotated #fastapi String validation #fastapi max_length #fastapi min_length #fastapi regex #fastapi default #fastapi ellipsis #fastapi list #fastapi title #fastapi description #fastapi metadata
댓글남기기